Why Every Home Needs the Fire + Burn Care Kit (And How to Use It) Burns are one of the...
Knowing how to handle different types of fire is crucial to keeping your loved ones safe. Class C fires are one of the most dangerous types because they’re fueled by electricity. They’re also hard to predict because the warning signs are subtle. Plus, the National Fire Protection Administration (NFPA) reports an average of 46,700 electrical home fires occur every year.
But what exactly are Class C fires? How do they start? What causes them? How do you put them out? Find out everything you need to know about Class C fires below.
What Are Class C Fires?
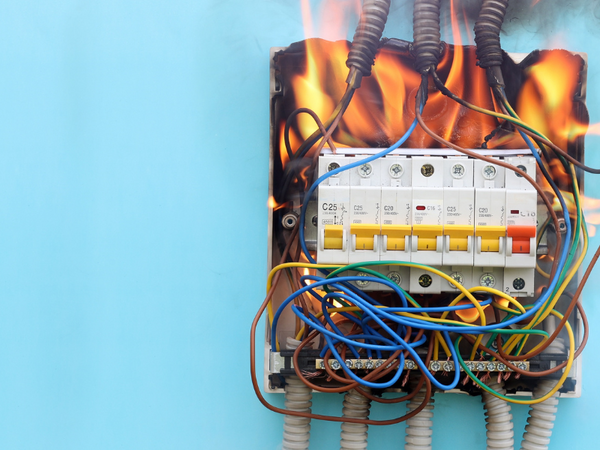
A Class C fire is a type of fire caused by electrical equipment. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) defines Class C fires as fires involving energized electrical equipment.
As long as the electrical equipment is connected to a live power source, the Class C fire can continue. Until the power is turned off, the fire will continue damaging other equipment and spreading to other areas.
What makes Class C fires dangerous is how fast they spread. Once the electrical equipment catches fire, it can quickly spread to other areas or explode. Contrary to popular belief, they’re not limited to homes. Class C fires can also start in industrial settings and even outdoors. Since many wires are hidden behind walls, people may not notice the fire until it’s too late. This makes Class C fires hard to detect since being behind walls or ceilings gives them more time to grow and cause more damage before someone can respond.
In addition, electrical fires can lead to explosions, which can cause injuries, property damage, and death. How quickly these fires grow also leaves little time for people to escape, which increases the risk of injury and death. Once a Class C fire starts, it can spread quickly because wires are connected all over a house or building. If the fire isn’t contained or the power source isn’t shut off, the fire will continue to burn and consume everything in its path.
Water doesn’t help, either. Since water is a good conductor of electricity, water and water-based extinguishers cannot put out a Class C fire. In fact, using water on a Class C fire can electrocute the person trying to put it out.
Common Causes of Class C Fires

Here are the common fuels that cause Class C fires. We’ll also talk about how dangerous they are and how they can start Class C fires.
1. Faulty Wiring
Old, damaged, or exposed wires can start Class C fires in your home. Wires can fray or become loose over time, resulting in sparks that can ignite nearby fire hazards. These fires can start small but spread quickly, especially when hidden behind walls or in ceilings.
The same principle applies when you install new lights or appliances without safe connections. They may flicker, cause the circuit to trip, or produce sparks that can turn into dangerous electrical fires.
2. Overloaded Outlets
We’ve all been there—plugging too many devices into a single outlet to charge phones, tablets, and laptops. Overloaded outlets can start electrical fires, especially in houses where a lot of electricity is used. This is common, especially in areas with many appliances like living rooms or kitchens.
3. Malfunctioning Appliances
Appliances like fridges, toasters, and microwaves make our lives easier, but they also pose fire risks. Let’s say your toaster suddenly starts smoking while you’re making breakfast. It then produces sparks that land on your paper towels. The fire then spreads to other flammable items in your kitchen, including curtains, cleaning rags, and boxes. Whether it’s a short circuit in your toaster or a faulty coffee maker, a Class C fire can start from any appliance.
4. Heating Devices
As the temperature drops, people use space heaters, electric blankets, and other heating devices to stay warm. The fire risk increases during colder months when people use them more frequently.
Picture this: it’s a cold winter night, and you’ve set up a space heater near your couch to keep warm. If it accidentally tips over or is placed too close to a candle, it could start an electrical fire.
5. Overheating Electronics
In today’s tech-driven world, we heavily use electronics like computers, printers, and gaming consoles. Unfortunately, these devices can overheat or malfunction and start a Class C fire. Think about this: your computer suddenly starts making strange noises and emits smoke. This means it’s malfunctioning and could start a Class C fire. While often preventable, not having the right knowledge or tools puts everyone at risk.
Where Do Class C Fires Happen?

Class C fires can happen almost anywhere, but they’re more likely to start in certain places. Here are the most common locations where Class C fires occur:
Kitchens
Kitchens are hot spots for Class C fires because of the appliances present. Think about ovens, microwaves, coffee makers, ovens, and toasters. If a toaster overheats or a microwave malfunctions, a Class C fire might break out. For example, if food gets stuck in a toaster and it heats up when you turn it on, a fire can start.
Living Areas
Living rooms contain many electrical devices—TVs, chargers, speakers, lamps, and more. If a power strip is overloaded or an extension cord gets damaged, An electrical fire might occur. Think about a lamp with exposed wires that catches the couch on fire. This is why you should regularly check cords, appliances, and devices for wear and tear.
Offices
Offices also contain different electrical equipment, such as computers, printers, and copiers. These devices can malfunction if too many are plugged into one outlet. For example, a printer might overheat because of continuous use or a short circuit. It can ignite the paper loaded into it and start a Class C fire. Cables can also get damaged under desks and expose wires that produce sparks.
Workshops and Garages
Workshops and garages are filled with electric tools and machines. Imagine a power drill that sparks while in use. If it’s near flammable materials like sawdust or wood, it could easily start a fire. Nearby flammable items like gasoline, butane, and oil rags can accelerate the fire.
Data Centers
Data centers are filled with servers and computers, all of which require a lot of power. If a server overheats due to poor ventilation or a power surge, it can catch fire. For example, a faulty power supply unit in a server room might short-circuit and burn nearby computers and cables.
Manufacturing Plants
Manufacturing facilities are filled with huge machines and electrical tools. A malfunctioning conveyor belt motor, for example, could overheat and spark a fire. If that happens near flammable materials, you’ve got a recipe for disaster. Poor machine maintenance can also lead to malfunction, so workers should be trained to identify risks and hazards associated with fire.
Hotels
Hotels contain many electrical appliances, from mini-fridges to hair dryers. For example, leaving a hair dryer on near flammable items like tissue and hair sprays can lead to a Class C fire. Plus, hotels have lots of rooms, so the fire can escalate quickly.
How to Put Out Class C Fires

Knowing how to put out Class C fires keeps your loved ones and co-workers safe. They can cause severe damage if you don’t act quickly. Here’s how to put out Class C fires:
1. Stay calm.
Don’t panic if you see a Class fire. Panic can lead to poor judgment and make things worse. So, take a deep breath and see if you can handle the fire. If yes, proceed to the next step. Otherwise, exit your house or building. Remember, your safety is the priority here. We also recommend following the RACE protocol if possible.
2. Turn off the power supply.
Class C fires will continue burning if there’s fuel, heat, and oxygen. Removing at least one of them can put out the fire. Turning off the power source stops the electricity from sustaining the fire. Only turn off the power source if it’s safe to do so. Otherwise, put your safety first and evacuate.
3. Use the right tools.
You can use a fire blanket, vapor or dry fire spray, and electrical fire extinguisher to put out Class C fires.
A fire blanket puts out a small Class C fire by depleting the fire of oxygen. Since it can remove gas from the equation, it can remove the fuel. Simply grab the blanket and carefully cover the fire with it.
If you can’t safely go near the affected area to use a fire blanket, use a fire spray or fire extinguisher instead. Aim the nozzle at the base of the fire and spread from side to side to put out the flames. Check out the PASS fire extinguisher protocol here.
4. Check hot spots.
Keep an eye on the area after the fire dies. Class C fires can reignite if left unattended too quickly. Use a fire blanket, fire spray, or fire extinguisher if you notice any signs of the fire reigniting.
5. Call the fire department.
If the fire grows and spreads quickly despite using the tools above, evacuate and call the fire department immediately. Even if the fire seems to be decreasing, call them still. The fire department can inspect the area and make sure everything’s safe.
How to Prevent Class C Fires

Keeping an eye on flammable gases helps protect your home and workplace from Class C fires. Plus, being proactive gives you peace of mind and keeps everyone safe. Here’s how to prevent Class C fires:
1. Know Your Connections
Be familiar with the wires and outlets at home or work, especially those found behind walls and ceilings. Know where the switches are, the main power source, and the appliances they’re connected to.
2. Check for Electrical Issues
Regularly inspect your home or workplace for electrical issues. Have certified electricians check everything, and watch out for sparks and hissing sounds. If you notice anything off, call a professional immediately.
3. Install Smoke Detectors
Install smoke detectors in high-risk areas. These detectors can warn you about electrical fires, giving you enough time to respond. Learn more about the types of smoke detectors here.
4. Maintain Equipment
Regularly maintain electrical appliances like ovens, heaters, and grills. Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines to prevent them from malfunctioning. You can also have a professional come in to check them from time to time.
5. Keep Flammables Away
Keep flammable items away from electrical appliances. Store items like paper, fabric, and other fire hazards far from them to prevent ignition.
6. Educate Others
Make sure everyone in your house or workplace knows about the dangers of electrical issues and what to do in case of a fire. Regularly conduct fire drills and training to keep this knowledge fresh. Learn why it’s important to understand the risks and hazards associated with fire here.
Conclusion
Class C fires can happen out of nowhere and spread fast. Knowing what fuels them—like propane, butane, and methane—helps you stay safe and be prepared. Regularly checking for gas leaks, properly storing flammable gases, and having the right tools also help.
Do you want reliable, easy-to-use, and affordable tools to help you deal with Class C fires? Check out Prepared Hero’s fire prevention tools here, and get up to 51% off on certain items. Stay safe, hero!


 Fire
Fire Safety
Safety Survival
Survival Protection
Protection New
New Scouting America
Scouting America
 Fire
Fire Safety
Safety Survival
Survival Protection
Protection New
New












